What Is Physical AI and Why Does It Matter?
Physical AI is emerging as a buzzword in the future of transportation and mobility sectors. Unlike conventional AI, which operates in purely digital environments, Physical AI integrates artificial intelligence directly with physical systems—robots, vehicles, or even infrastructure—with the promise to revolutionize how machines interact with the real world.
This goes beyond software algorithms to involve tangible elements working in dynamic environments. For many, this represents a new frontier where AI-powered machines adapt in real time, offering more autonomy and flexibility. But is this truly transformative, or is it just hype riding the wave of AI fascination?
How Does Physical AI Work?
At its core, Physical AI combines machine learning with embedded sensors, actuators, and control systems. These physical components allow AI algorithms to perceive, evaluate, and act on their environment without human intervention.
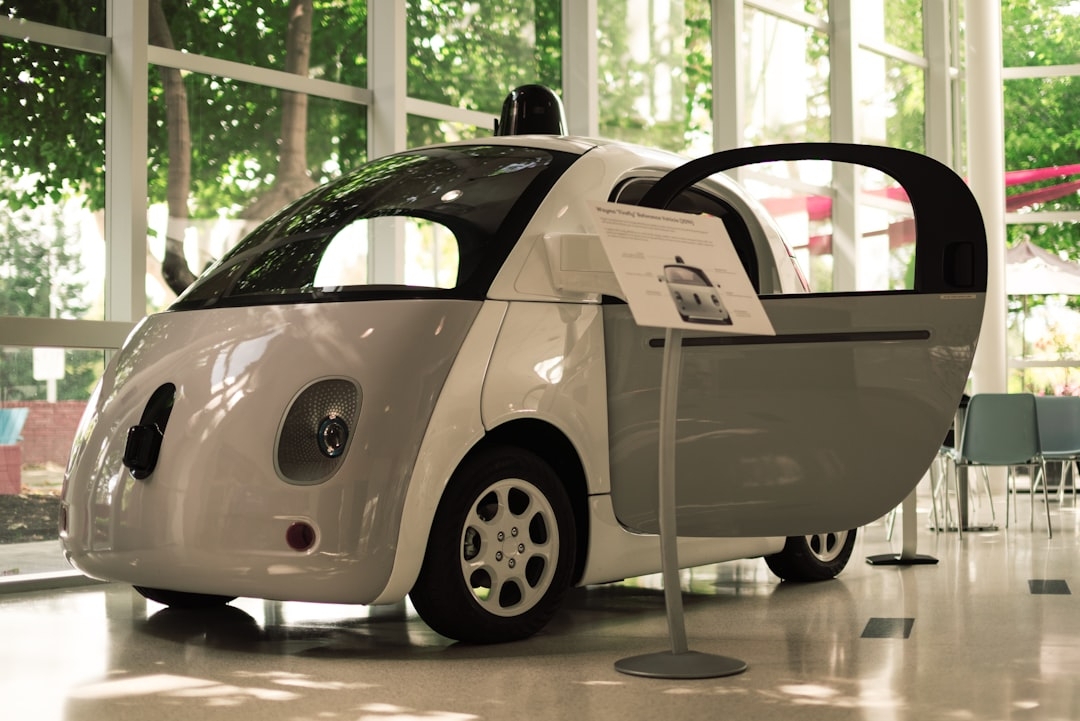
Think of a self-driving car: its AI isn’t just interpreting data in a server farm but directly controlling steering, braking, and acceleration in response to traffic conditions. Physical AI extends that principle further, often requiring real-time feedback loops between sensors and effectors.
Technical terms in this space include:
- Actuators: Devices that physically move parts of the AI system, e.g., motors.
- Sensors: Inputs that collect data from the environment, from cameras to temperature sensors.
- Feedback loops: Continuous cycles where sensor data influences actuator responses instantaneously.
While elegantly simple in concept, these systems often face messy real-world constraints like latency, hardware failures, and unpredictable environments.
Is Physical AI Just Hype? The Problem With Current Expectations
There’s no doubt that Physical AI is an exciting vision, but from direct experience, caution is warranted. Many early implementations promise seamless adaptability and near-human intuition, but reality exposes serious limitations.
Developers often underestimate integration complexity—combining software intelligence with physical mechanics adds layers of uncertainty. Unlike software-only AI, where bugs can be patched easily, Physical AI faults can involve hardware malfunctions or safety risks.
The hype machine also glosses over:
- High research and development costs
- Difficulty in scaling from prototypes to production-ready models
- Challenges in maintaining robust perception under varying environmental conditions
When Should You Consider Using Physical AI?
Physical AI might be worth the investment under specific conditions where traditional automation fails or proves inefficient:
- If the task requires continuous adaptation to unstructured, evolving environments
- Where human presence is risky or impossible, such as hazardous industrial sites
- When you need high precision and responsiveness beyond current robotic capabilities
However, avoid rushing in solely because the term is trendy. Evaluate carefully if the technology meets your real-world operational requirements rather than theoretical capabilities.
How Is Physical AI Being Implemented in Mobility Today?
Several companies and research labs have dipped toes into Physical AI applications:
- Robotic delivery vehicles that navigate sidewalks autonomously
- Adaptive manufacturing robots that reconfigure tasks dynamically
- Self-driving cars using integrated AI sensors to handle complex urban environments
Despite these advances, many projects remain in pilot stages. Deployment hurdles include regulatory approval, safety assurance, and long-term reliability studies. This often means technology readiness is lower than publicized.
Practical Considerations
Before committing resources, consider the following:
- Time frame: Physical AI projects often take years to mature from lab to market-ready.
- Costs: Hardware and integration expenses can balloon quickly, especially with custom solutions.
- Risks: Physical failures pose safety and liability challenges far exceeding those of software alone.
- Constraints: Environmental unpredictability can degrade system performance dramatically.
How Can You Evaluate If Physical AI Fits Your Needs?
Given the complexity and hype, a quick evaluation framework is essential. In 10-20 minutes, stakeholders can assess feasibility by:
- Defining concrete objectives where Physical AI could add value
- Listing key environmental challenges your application faces
- Mapping necessary physical components and available sensor technologies
- Estimating upfront costs vs. potential long-term savings or capabilities
- Considering regulatory or safety barriers specific to your sector
This pragmatic approach cuts through marketing hype and grounds decisions in operational reality.
The Verdict: Physical AI Is Neither Magic Nor Myth
Physical AI represents a bold evolution from purely digital intelligence to embodied systems that interact dynamically with the physical world. It is not mere hype, but it is far from a silver bullet.
The technology demands significant investment, technical expertise, and patience. Many proof-of-concept projects have stalled or failed when confronted with real-world unpredictability. Success hinges on rigorous evaluation of operational needs, risks, and implementation challenges.
The road ahead will see incremental advances, not overnight revolutions. For practitioners, tempered expectations paired with critical assessment can avoid costly missteps while harnessing Physical AI’s potential where it truly fits.
Quick Action: A 15-Minute Physical AI Feasibility Checklist
- Identify specific use cases where Physical AI might excel in your operations.
- Assess environmental variables influencing physical interactions, e.g., lighting, weather.
- Catalogue existing hardware and gaps to integrate sensors and actuators.
- Estimate upfront and ongoing costs including maintenance and safety compliance.
- Evaluate organizational capability to manage cross-disciplinary challenges.
Use this checklist as a starting point to decide if Physical AI is a worthwhile pursuit or a distraction in your mobility innovation strategy.
Technical Terms
Glossary terms mentioned in this article














Comments
Be the first to comment
Be the first to comment
Your opinions are valuable to us